Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (31): 5044-5049.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.31.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hip arthroplasty and internal fixation for the repair of femoral neck fracture in the elderly patients: a meta-analysis of reoperation and complications
Ji Ning, Sun Zhen-hui, Jiang Ze-hua, Zhang Yu, Wang Lei, Zhang Xue-li
- Department of Spine Surgery, Tianjin Municipal People’s Hospital, Tianjin 300121, China
-
Received:2014-07-04Online:2014-07-23Published:2014-07-23 -
Contact:Zhang Xue-li, Chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Tianjin Municipal People’s Hospital, Tianjin 300121, China -
About author:Ji Ning, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Spine Surgery, Tianjin Municipal People’s Hospital, Tianjin 300121, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ji Ning, Sun Zhen-hui, Jiang Ze-hua, Zhang Yu, Wang Lei, Zhang Xue-li. Hip arthroplasty and internal fixation for the repair of femoral neck fracture in the elderly patients: a meta-analysis of reoperation and complications[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(31): 5044-5049.
share this article
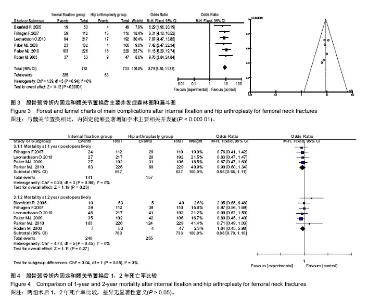
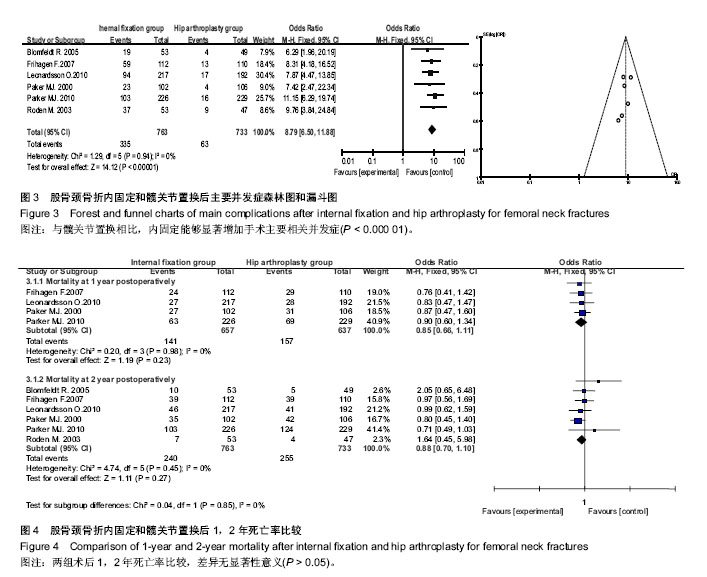
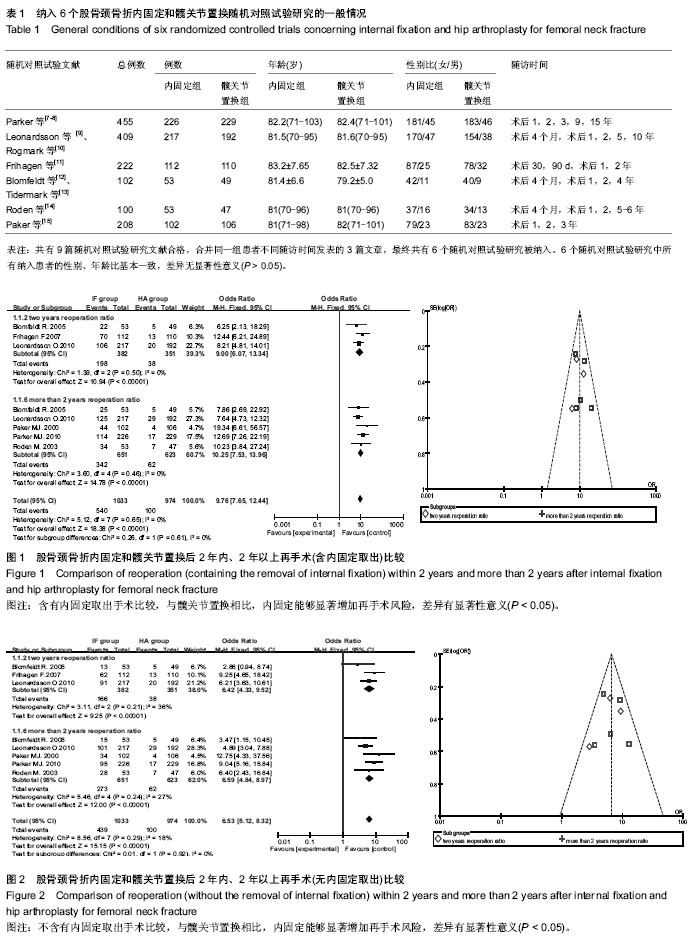
2.1 文献检索结果 经全面计算机及手工检索,共检索到356篇临床试验文献:PubMed检索获得文献36篇,Embase检索获得文献275篇,Cochrane CENTRAL检索获得文献48篇。共有9篇随机对照试验研究文献合格[7-15],合并同一组患者不同随访时间发表的3篇文章,最终共有6个随机对照试验研究被纳入,均为英文文献。样本总量合计1 496例。各纳入研究的基本情况见表1。纳入研究的6个随机对照试验中患者的年龄、性别比基本资料经统计学检验在基线水平上一致。6个随机对照试验文献质量等级均为低风险。 2.2 Meta分析结果 2.2.1 再手术情况比较 含有内固定取出手术比较:共3个随机对照试验报道了术后2年内再手术情况,内固定组198例,髋关节置换组38例,发生率分别为51.8%和10.8%,各研究间无统计学异质性(P=0.50,I2=0%),固定效应Meta分析表明与髋关节置换相比,内固定显著增加了再手术 [OR=9.00,95% CI(6.07-13.34),P < 0.000 01]。术后2年以上再手术情况(共5个随机对照试验报道),内固定组342例,髋关节置换组62例,发生率分别为52.52%和9.95%,各研究间无统计学异质性(P=0.46,I2=0%),固定效应Meta分析表明与髋关节置换相比,内固定显著增加了再手术[OR=10.25,95% CI(7.53-13.96),P < 0.000 01]。两个亚组合并后共有8个随机对照试验报道,内固定组540例,髋关节置换组100例,发生率分别为52.3%和10.3%,各研究间无统计学异质性(P=0.65,I2=0%),固定效应Meta分析表明与髋关节置换相比,内固定能够显著增加再手术风险[OR=9.76,95% CI(7.65-12.44),P < 0.000 01]。Meta 分析结果稳定,倒漏斗图显示基本对称(图1)。 不含有内固定取出手术比较:术后2年内再手术内固定组166例,髋关节置换组38例,发生率分别为43.5%和10.8%,各研究间无统计学异质性(P=0.21,I2=36%),固定效应Meta分析表明与髋关节置换相比,内固定显著增加再手术[OR=6.42,95%CI(4.33-9.52),P < 0.000 01]。术后2年以上再手术内固定组273例,髋关节置换组62例,发生率分别为41.9%和10.0%,各研究间无统计学异质性(P=0.24,I2=27%),固定效应Meta分析表明与髋关节置换相比,内固定显著增加再手术[OR=6.59,95%CI (4.84-8.97),P < 0.000 01]。两个亚组合并后内固定组再手术439例,髋关节置换组100例,发生率分别为42.5%和10.3%,各研究间无统计学异质性(P=0.29,I2=18%),固定效应Meta分析表明与髋关节置换相比,内固定能够显著增加再手术[OR=6.53,95%CI(5.12-8.32),P < 0.000 01]。Meta分析结果稳定,倒漏斗图显示基本对称(图2)。 2.2.2 手术相关主要并发症比较 6个随机对照试验均报道了股骨颈骨折术后手术相关主要并发症,内固定组335例,髋关节置换组63例,发生率分别为43.9%和8.6%,各研究间无统计学异质性(P=0.94,I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型Meta分析。结果显示:老年股骨颈骨折与髋关节置换相比,内固定能够显著增加手术主要相关并发症[OR=8.79,95%CI (6.50-11.88),P < 0.000 01]。Meta分析结果稳定,倒漏斗图显示基本对称(图3)。 2.2.3 股骨颈骨折术后死亡率比较 ①术后1年内死亡率:共4个随机对照试验报道了术后1年内死亡率,内固定组141例,髋关节置换组157例,发生率分别为21.5%和24.7%,各研究间无统计学异质性(P=0.98,I2=0%),固定效应Meta分析表明老年股骨颈骨折髋关节置换和内固定相比,术后1年内死亡率差异无显著性意义[OR=0.85,95%CI(0.66-1.11),P=0.23]。②术后2年内死亡率:6个随机对照试验均报道了术后2年内的死亡率,内固定组240例,髋关节置换组255例,发生率分别为31.5%和34.8%,各研究间无统计学异质性(P=0.45,I2=0%),固定效应Meta分析表明老年股骨颈骨折髋关节置换和内固定相比,术后2年内死亡率差异无显著性意义[OR=0.88,95%CI (0.70-1.10),P=0.27,见图4]。"
| [1] Bilsel K,Erdil M,Gulabi D, et al. Factors affecting mortality after hip fracture surgery: a retrospective analysis of 578 patients. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23(8):895-900. [2] Fisher MA,Matthei JD,Obirieze A, et al. Open reduction internal fixation versus hemiarthroplasty versus total hip arthroplasty in the elderly: a review of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database. J Surg Res. 2013; 181(2):193-198. [3] SooHoo NF,Farng E,Chambers L, et al. Comparison of complication rates between hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty for intracapsular hip fractures. Orthopedics. 2013; 36(4):e384-389. [4] Dai Z,Li Y,Jiang D. Meta-analysis comparing arthroplasty with internal fixation for displaced femoral neck fracture in the elderly. J Surg Res. 2011;165(1):68-74. [5] Zielinski SM,Meeuwis MA,Heetveld MJ, et al. Adherence to a femoral neck fracture treatment guideline. Int Orthop. 2013. [6] Rogmark C, Carlsson A, Johnell O, et al. Primary hemiarthroplasty in old patients with displaced femoral neck fracture: a 1-year follow-up of 103 patients aged 80 years or more. Acta Orthop Scand. 2002;73(6):605-610. [7] Parker MJ,Pryor G,Gurusamy K. Hemiarthroplasty versus internal fixation for displaced intracapsular hip fractures: a long-term follow-up of a randomised trial. Injury. 2010; 41(4): 370-373. [8] Parker MJ,Khan RJ,Crawford J, et al. Hemiarthroplasty versus internal fixation for displaced intracapsular hip fractures in the elderly. A randomised trial of 455 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(8):1150-1155. [9] Leonardsson O,Sernbo I,Carlsson A, et al. Long-term follow-up of replacement compared with internal fixation for displaced femoral neck fractures: results at ten years in a randomised study of 450 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010; 92(3):406-412. [10] Rogmark C,Carlsson A,Johnell O, et al. A prospective randomised trial of internal fixation versus arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the neck of the femur. Functional outcome for 450 patients at two years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(2):183-188. [11] Frihagen F,Nordsletten L,Madsen JE. Hemiarthroplasty or internal fixation for intracapsular displaced femoral neck fractures: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2007; 335 (7632):1251-1254. [12] Blomfeldt R,Tornkvist H,Ponzer S, et al. Comparison of internal fixation with total hip replacement for displaced femoral neck fractures. Randomized, controlled trial performed at four years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(8):1680-1688. [13] Tidermark J,Ponzer S,Svensson O, et al. Internal fixation compared with total hip replacement for displaced femoral neck fractures in the elderly. A randomised, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(3):380-388. [14] Roden M,Schon M,Fredin H. Treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures: a randomized minimum 5-year follow-up study of screws and bipolar hemiprostheses in 100 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74(1):42-44. [15] Parker MJ,Pryor GA. Internal fixation or arthroplasty for displaced cervical hip fractures in the elderly: a randomised controlled trial of 208 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(5): 440-446. [16] Chammout GK,Mukka SS,Carlsson T, et al. Total hip replacement versus open reduction and internal fixation of displaced femoral neck fractures: a randomized long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(21):1921-1928. [17] Soreide O,Molster A,Raugstad TS. Internal fixation versus primary prosthetic replacement in acute femoral neck fractures: a prospective, randomized clinical study. Br J Surg. 1979;66(1):56-60. [18] El-Abed K,McGuinness A,Brunner J, et al. Comparison of outcomes following uncemented hemiarthroplasty and dynamic hip screw in the treatment of displaced subcapital hip fractures in patients aged greater than 70 years. Acta Orthop Belg. 2005;71(1):48-54. [19] Rogmark C,Carlsson A,Johnell O, et al. Costs of internal fixation and arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: A randomized study of 68 patients. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica. 2003; 74(3):293-298. [20] Johansson T,Jacobsson SA,Ivarsson I, et al. Internal fixation versus total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures: a prospective randomized study of 100 hips. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(6):597-602. [21] Johansson T. Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures A prospective randomized study of clinical outcome, nutrition and costs. Thesis English. 2002. [22] Johansson T,Bachrach-Lindstrom M,Aspenberg P, et al. The total costs of a displaced femoral neck fracture: comparison of internal fixation and total hip replacement. A randomised study of 146 hips. Int Orthop. 2006; 30(1):1-6. [23] Jain NB,Losina E,Ward DM, et al. Trends in surgical management of femoral neck fractures in the United States. Clin Orthop Relat Rese. 2008;466(12):3116-3122. [24] Lee YK,Ha YC,Park C, et al. Trends of Surgical Treatment in Femoral Neck Fracture. A Nationwide Study Based on Claim Registry. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(10):1839-1841. [25] Lu-Yao GL,Keller RB,Littenberg B, et al. Outcomes after displaced fractures of the femoral neck. A meta-analysis of one hundred and six published reports. J Bone Joint Surg. 1994; 76(1):15-25. [26] Gao H,Liu Z,Xing D, et al. Which is the best alternative for displaced femoral neck fractures in the elderly?: A meta-analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(6):1782-1791. [27] Bhandari M,Devereaux PJ,Swiontkowski MF, et al. Internal fixation compared with arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the femoral neck: A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg. 2003;85(9):1673-1681. |
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [11] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [12] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [13] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Han Shufeng. Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||